A Complete Beginner’s Guide to Technical SEO

Ever Think about why some websites rank on Google’s first page while others with great content remainburied? The secret often lies in Technical SEO – the foundation that makes your website discoverable, crawlable, and lovable to search engines.
If you’re new to technical SEO, don’t worry. This guide breaks down everything you need to know into simple, actionable steps. By the end, you’ll understand how to make your website technically soundand ready to climb search rankings.
What you’ll learn:
- What technical SEO is and why it matters?
- Why Technical SEO important?
- Technical SEO For AI Search.
- How search engines crawl and index websites?
- Core technical elements (site speed, mobile optimization, structured data)
- Practical tools and checklists to audit your site.
Quick wins to implement to do Lets dive in:
What is Technical SEO?
Technical SEO is the process of optimizing your website’s infrastructure to help search engines crawl,index, and understand your content more effectively. Think of it as building a solid foundation for a house without it, nothing else stands properly.Unlike content-focused on-page SEO or link-building off-page SEO, technical SEO deals with thebackend elements: site speed, mobile responsiveness, XML sitemaps, robots.txt files, and more.
Why Technical SEO Impotant?
Technical SEO is important because it ensures your website is discoverable, crawlable, and comprehensible to search engines serving as the invisible foundation supporting all your online efforts. Without it, even well-written content and solid design may fail to reach the right audience, since search engines could struggle to access, index, or rank your pages effectively. Hence,Technical SEO play most important role for ranking your website.
Technical SEO is the essential backbone that lets your site stand out in search, deliver a great user experience, and grow sustainably providing long-lasting visibility, better engagement, and higher returns after initial optimization.
Technical SEO For AI Search
Technical SEO plays a decisive role in ranking your website in AI-powered search results by making your site accessible, understandable, and trustworthy to both traditional search engines and new AI-driven platforms like Google’s AI Overviews, Perplexity, Gemini, Bing Copilot, and more.Nowdays AI search relies not just on keyword matching, but on deep analysis of your site’s structure, data clarity, and technical foundations.So,Technical SEO is the foundation for both conventional search and AI-powered results.To know the official news changes and information about seo and AI follow the Google search central.
How search engines crawl and index websites?
Crawling:
Crawling is how search engines discover pages. Google’s bots (called Googlebot) follow links from page to page, discovering new and updated content.
Key Points:
- Googlebot starts with known URLs and follows internal/external links
- Your robots.txt file tells bots what to crawl (or not crawl)
- Crawl budget determines how many pages Google crawls per visit.
Google’s crawl budget refers to the number of URLs that Googlebot wants to crawl on a website within a given timeframe, determined by crawl rate limits and crawl demand.
Indexing:
Indexing is the process by which search engines organize, analyze, and store crawled web page content in their databases so that it can be quickly and easily retrieved in response to search queries. After search engines crawl a website and gather content, they index these pages to make them accessible and searchable by users.
After crawling, Google indexes pages – storing them in a massive database. Not every crawled page gets indexed. Google evaluates:
- Content quality and uniqueness
- Technical accessibility (no noindex tags, proper canonicals)
- Page value to users
To know your page index or not use free technical seo tool like google search console and free Ahrefs webmaster tool. By using these tool you can easily found the problem why your site can’t index in google.
Robert.text:
A robots.txt file is a simple text file placed in the root directory of a website that tells search engine crawlers (bots) which parts of the website they are allowed to visit and which parts they should avoid crawling.
Robots.txt File Optimization:
The robots.txt file lives at yoursite.com/robots.txt and tells crawlers which pages to access.
Example robots.txt:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /admin/
Disallow: /private/
Allow: /
Sitemap: https://yoursite.com/sitemap.xml
Best practices:
- Don’t block important pages by mistake,
- Use robots.txt to hide duplicate content or admin pages
- Test with Google Search Console’s robots.txt tester
Rendring:
Rendering in web development and SEO refers to the process by which a web browser or search engine crawler processes the code of a webpage—HTML, CSS, and JavaScript—and transforms it into the visual, interactive page that users see on their screens. This involves building the Document Object Model (DOM) from the HTML, parsing the styling from the CSS (CSSOM), combining these into a Render Tree, calculating layouts for each element, and painting the final page on the user’s device.If rendering fails, Google sees an incomplete page, hurting for rankings.
Then, Finally, Google ranks indexed pages based on relevance, authority, and user experience. Technical factors like Core Web Vitals, mobile-friendliness, and HTTPS all influence rankings.
Core technical elements (site speed, mobile optimization, structured data)
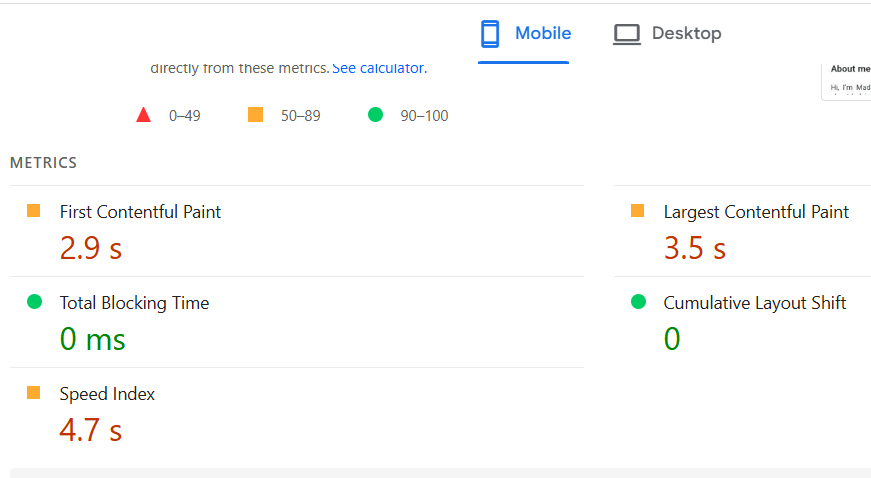
Site Speed:
Site speed optimization refers to the process of improving how quickly web pages load and become interactive for users. A faster website delivers a better user experience, reduces bounce rates, and positively impacts search engine rankings since site speed is a confirmed ranking factor for SEO. See and check core web vitals for site speed cheking in google search counsole its a free research tool.
Key methods for optimizing site speed include:
- Compressing Images and Media: Use modern formats like WebP or shortpixel.com tools to reduce file sizes without losing quality.
- Minimizing and Combining Files: Reduce CSS, JavaScript, and HTML file sizes through minification and combine files to reduce HTTP requests.
- Using Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): Distribute content geographically closer to users for faster delivery.
- Reducing Server Response Time: Optimize backend processing and use faster hosting or server configurations.
- Prioritizing Critical Content: Lazy-load images and defer non-critical scripts to focus first on visible content.
- Enabling Compression: Use GZIP or Brotli to compress files sent from the server to reduce transfer sizes.
- Implementing Efficient Code: Avoid excessive JavaScript, use lightweight frameworks, and reduce render-blocking resources.
Monitoring tools like Google PageSpeed Insights, GTmetrix, and Chrome DevTools help identify specific bottlenecks and provide actionable recommendations.
Mobile optimization:
Mobile optimization means making your website work well on mobile devices like smartphones and tablets. It ensures that visitors can easily read, navigate, and interact with your site without any problems, providing a good experience regardless of the device they use. Check mobile speed screen test in free tools like pagespeed insight.
Simple Examples of Mobile Optimization:
- Responsive Design: Your website adjusts automatically to fit different screen sizes. For example, images and text resize to look good on both small phones and large tablets without zooming or horizontal scrolling
- Fast Loading Speed: Compress images and minimize heavy code so pages load quickly on mobile networks, which are usually slower than desktop connections.
- Easy Navigation: Make menus simple and buttons large enough to tap comfortably. Avoid hidden menus and pop-ups that cover the content.
- Readable Text: Ensure text is large enough to read without zooming, and line spacing is comfortable.
- Avoid Intrusive Pop-ups: Don’t show pop-ups immediately when a visitor opens your page, especially those covering the main content.
Structure data:
Structured data, also known as schema markup, is a special code you add to your website’s HTML that helps search engines understand what your content is about. It organizes information in a clear, standardized format, making it easier for search engines to display rich results like star ratings, reviews, events, and other features in search listings.
For example, if you run a restaurant website, you can use schema markup to tell search engines your restaurant’s name, address, menu, and reviews. When people search for your restaurant, Google can show this extra information directly in the search results, making your listing more attractive and informative.There are different ways to add schema markup, but the most recommended method is JSON-LD, which is simple, flexible, and placed in the <head> section of your webpage
HTML Sitemap:
An HTML sitemap is a regular web page on your site that lists important pages (like Home, About, Contact, Products, or Blog posts) in a clear, clickable list. Think of it as a table of contents for your website, designed to help visitors quickly find any page they need—especially useful on large sites or when menus get complicated.
- User-focused: Unlike XML sitemaps (made for search engines), HTML sitemaps are created for people to use.
- Easy navigation: Visitors see all key sections of your site at a glance and can jump straight to what they want.
- Usually linked in the footer so users can easily find it.
Practical tools and checklists to audit your site.
As a beginner in technical seo most recommended use is free tools. After mastering free tools, use a paid tool. This is the right track for your SEO journey.
Here are list of free tools:
1.Google search Counsole: Use Google Search Console for checking the crawling, indexing, and all core web vitals to know if your page is indexed or not. And fixing all the technical issues and finding the broken links on the pages.
2.Pagespeed insight: Use pagespeed insight for testing the mobile and desktop speed test and others.
3.Ahrefs webmaster tools: It is also on of the best free tools for find out the problems and all issuse of technical seo.
4.Google Analytics(GA4): is the latest web analytics platform from Google, which helps track user behavior on websites and apps in a unified manner.It collects detailed data about how visitors interact with your site such as page views, clicks, scrolls, and conversions and provides insights to improve SEO and website performance.
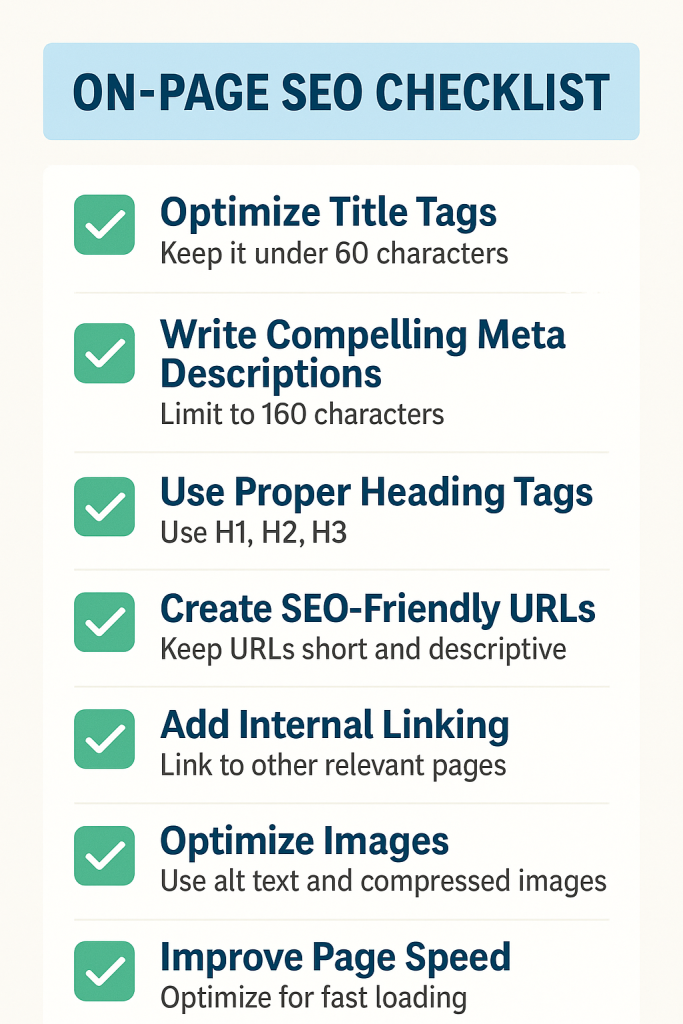
Here is free Technical SEO checklist:
Beginner Level
- Configure a proper robots.txt file to control crawler access.
- Create and submit an XML sitemap to search engines.
- Check indexing status of important pages in Google Search Console.
- Fix crawl errors and broken links.
- Ensure all pages have appropriate meta robots tags (use “noindex” where needed).
- Use clean, descriptive URLs.
- Set canonical URLs to prevent duplicate content issues.
- Make sure your site is mobile-friendly with responsive design.
- Use HTTPS to secure your website.
- Check and improve page loading speed.
- Add structured data (schema markup) to key pages (JSON-LD preferred).
- Avoid duplicate title tags and meta descriptions.
- Optimize image size and include descriptive alt text.
- Use descriptive heading tags (H1, H2, etc.) following hierarchy.
Intermediate Level
- Optimize internal linking structure for better crawlability and user navigation.
- Minimize redirect chains and fix redirect loops.
- Implement hreflang tags for multi-language or multi-region sites.
- Regularly audit for and fix broken backlinks or lost link equity.
- Implement or improve lazy loading for images and videos.
- Enable browser caching and file compression like GZIP.
- Use a CDN (Content Delivery Network) to improve global load times.
- Monitor and optimize Core Web Vitals (LCP, INP, CLS).
- Review server response times and optimize backend performance.
- Set up Google Analytics 4 (GA4) for detailed traffic and behavioral insights.
Advanced Level
- Conduct log file analysis to understand crawler behavior and optimize crawl budget.
- Perform JavaScript SEO audits to ensure important content loads and is crawlable.
- Use server-side rendering or pre-rendering for JavaScript-heavy sites.
- Fix orphaned pages not linked internally.
- Implement advanced structured data with full schema.org vocabulary coverage.
- Audit and fix content duplication beyond canonical tags (parameters, printer-friendly versions).
- Integrate AI SEO best practices, such as optimizing content for generative AI and ensuring crawlability for AI bots.
- Set up and monitor crawl budget management in Google Search Console.
- Use tools for continuous automated technical SEO auditing.
- Optimize for international SEO, covering domain structure, hreflang, and local content.
- Ensure all technical SEO changes comply with search engine guidelines to avoid penalties.
Conclusion:
Technical SEO might seem complex at first, but it’s the foundation that makes your website visible and understandable to search engines like Google. By ensuring your site is fast, easy to crawl, and well-structured, you’re setting yourself up for better rankings, more traffic, and happier visitors. Whether you’re just starting or looking to improve, mastering technical SEO gives you the power to unlock your website’s full potential. Remember, great content is important, but if search engines can’t find or understand it, it won’t reach your audience. Start with the basics, build your knowledge step by step, and watch your website climb the search results ladder with confidence.
FAQ (Bonus Section)
Q: How long does technical SEO take to show results?
A: Typically 3-6 months. Quick wins (fixing critical errors) can show improvements within weeks, butcomprehensive technical improvements take time for Google to recrawl and reassess.
Q: Do I need to know coding for technical SEO?
A: Basic HTML/CSS understanding helps, but many tools and CMS platforms (WordPress, Shopify) handle technical SEO with plugins. Focus on understanding concepts first.
Q: What’s the most important technical SEO factor?
A: There’s no single factor, but if you had to prioritize: ensure your site is crawlable, indexable, fast (Core Web Vitals), and mobile-friendly.
Q: How often should I run technical audits?
A: Monthly quick checks and quarterly comprehensive audits. Large or frequently updated sites benefit from monthly deep audits.
Q: Can I do technical SEO myself or hire an expert?
A: Basic technical SEO is DIY-friendly with tools like Google Search Console and PageSpeed Insights.Complex sites (large e-commerce, JavaScript-heavy) often benefit from expert help.